CPA vs CMA: What’s the Difference?
Aspiring accounting professionals may wonder what career path to take: certified public accountant (CPA) or certified management accountant (CMA). Both professions offer great opportunities, but they are distinct in their scope and requirements. In this blog, we will examine the differences between CPA vs CMA, including education requirements, salary ranges, and more.
What is a CPA?
A CPA is a licensed professional accountant who is authorized to practice public accounting. They are qualified to provide a broad range of accounting services, including auditing, financial analysis, and tax preparation for individuals, businesses, and government agencies. They can also provide consulting services and help clients make informed decisions based on financial data. CPAs are regulated by state boards of accountancy and must meet specific educational, experiential, and examination requirements to obtain their license.
What is a CMA?
A CMA, on the other hand, is an accounting professional who specializes in management accounting. They analyze financial data within organizations and provide advice on how to improve performance, reduce costs, and optimize resource allocation. They also play a strategic role in decision-making and often work closely with other departments such as marketing, operations, and human resources. CMAs are certified by the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA) and must pass a rigorous exam and meet specific educational and experience requirements.
CPA vs. CMA: Education Requirements
Both CPAs and CMAs need a bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field. However, additional education can be beneficial for both professions. A master’s degree in accounting or business administration can prepare individuals for the CPA and CMA exams and advance their careers.
For CPAs, the educational requirements vary by state but typically include at least 150 credit hours of coursework. This includes achieving the minimum number of accounting and business-related courses. Some states may also require candidates to have a certain number of accounting or business-related work experience, pass an ethics exam, and complete continuing education courses to maintain their license.
For CMAs, the educational requirements include a bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution or a recognized certification. Candidates must also have at least two years of work experience in management accounting, financial management, or a related field. They are required to pass a two-part exam that covers topics such as financial reporting, planning, analysis, and control.
CPA vs. CMA: Salary Range
The salary range for both professions varies based on factors such as years of experience, location, industry, and company size. According to the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA), the median annual salary for CPAs in the United States was $135,758 as of 2021. The IMA also reported that the median annual salary for CMAs was $122,000 as of 2021. However, individuals with both certifications saw a 49% increase in salary over those with neither certification—increasing their median salary to $140,000.
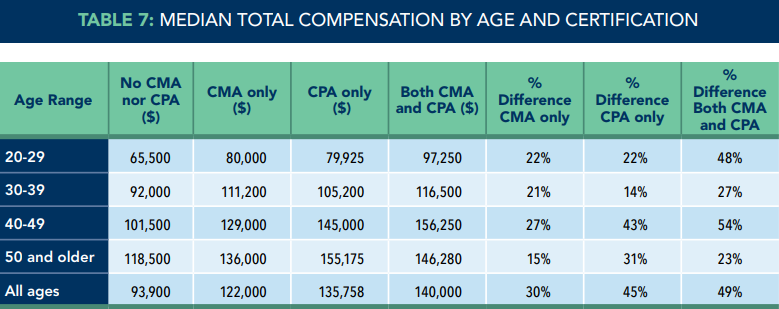
Salary Comparison imanet.org
CPA vs. CMA: Career Opportunities
CPAs have a wide range of career opportunities in public accounting, corporate accounting, government accounting, and consulting. They can work for accounting firms, businesses, and government agencies as auditors, tax professionals, financial analysts, forensic accountants, and consultants. They can also start their own accounting firm and provide a range of accounting services to clients.
CMAs have a more focused career path in management accounting and financial management. They work within organizations, analyzing financial data and providing insights to improve performance and profitability. They often work in roles such as cost accountants, financial analysts, budget analysts, and controllers.
Both the CPA and the CMA offer promising career opportunities and financial rewards. While both professions involve accounting, CPAs are licensed by their state and provide a range of services including tax preparation, auditing, and financial consulting, while CMAs specialize in management accounting and focus on providing financial information to help businesses make strategic decisions. Both professions require at least a bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field, but additional coursework and experience are required to become licensed or certified.
Your Next CPA or CMA Career Move is at Walsh College
In this blog, we explored the differences between the CPA and CMA specializations. The accounting field is full of unique specializations, opportunities, and niches for professionals to get involved in. And if you’re a detail-oriented person who loves making sense out of numbers, an accounting degree may be right for you. Whether you decide to pursue a CPA or CMA certification, the Bachelor of Science in accounting from Walsh College thoroughly prepares you for both exams—and your professional career beyond. Schedule an appointment with our enrollment team today to find out more.







